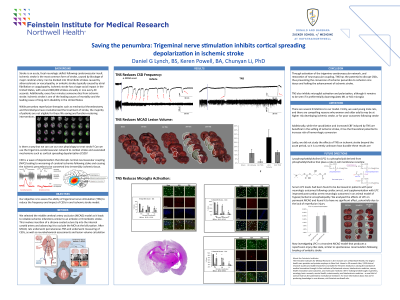
Neurobehavioral Deficits Predict Penumbra in a Preclinical Model of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Friday, April 21, 2023
.jpg)
Daniel G. Lynch
Medical Student Research Fellow
Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell
Long Island City, New York, United States
ePoster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a form of stroke that most often results from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm that spills blood into the surrounding tissue. In contrast with the well-established and predictable ischemic penumbra regions in ischemic stroke, this crucial therapeutic target has not yet been well-described in SAH. Considering that SAH may cause micro-infarcts and delayed cerebral ischemia far from the aneurysm rupture, and that these disruptions are closely linked to behavioral impairments, it is important to study the progression of penumbras. Notably, behavioral assessments can detect and approximately localize dysfunctional brain regions before permanent damages occur following SAH. Therefore, we hypothesized that the spatiotemporal distribution and progression of the core and penumbra in SAH may be predicted by specific patterns of behavioral impairment.
Methods: To test this hypothesis, we induced SAH using an endovascular filament perforation model, which is considered a close mimic of ruptured aneurysms in humans, and employed a behavioral battery at multiple time points followed by a histopathological analysis of brain tissue.
Results: Our results demonstrate that sensorimotor deficits occur early after SAH and remained static, while impairments in working memory, reference memory, exploration, and anxiety evolved in association with specific histologic lesions. All SAH rats displayed core infarctions in the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia and hypothalamus; whereas penumbras were found in the hippocampus (100%), thalamus (80%), and amygdala (60%).
Conclusion : Our study underscores the importance of identifying the penumbra regions following SAH and the utility of neurobehavioral tests for assessing multiple cognitive domains to detect and localize penumbra.
Methods: To test this hypothesis, we induced SAH using an endovascular filament perforation model, which is considered a close mimic of ruptured aneurysms in humans, and employed a behavioral battery at multiple time points followed by a histopathological analysis of brain tissue.
Results: Our results demonstrate that sensorimotor deficits occur early after SAH and remained static, while impairments in working memory, reference memory, exploration, and anxiety evolved in association with specific histologic lesions. All SAH rats displayed core infarctions in the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia and hypothalamus; whereas penumbras were found in the hippocampus (100%), thalamus (80%), and amygdala (60%).
Conclusion : Our study underscores the importance of identifying the penumbra regions following SAH and the utility of neurobehavioral tests for assessing multiple cognitive domains to detect and localize penumbra.
