Oral-specific and General-health Quality of Life Following a Subtemporal Preauricular Infratemporal Approach with Condylar Fossa Osteotomy in Surgical Skull-base Tumor Resection
Friday, April 21, 2023

Seika Taniguchi (she/her/hers)
2nd year Medical Student
University of British Columbia, British Columbia, Canada
ePoster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The subtemporal preauricular infratemporal approach (SPI) with condylar fossa osteotomy provides maximum lesion exposure and is thus favored in skull-based tumor resection – particularly skull-based chondrosarcomas (SBCs). However, the effects of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disruption in performing the condylar fossa osteotomy on oral-health quality of life (OQoL) is not well described. This study aims to evaluate the OQoL and general-health quality of life (GQoL) following SPI in SBC resection. Comparisons will be drawn to trigeminal schwannoma (TS) resection which follows the SPI approach without the condylar fossa osteotomy.
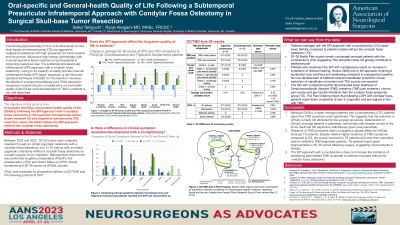
Methods: Between 2002 and 2022, 20 SBC patients and 14 TS patients were surgically managed by a single surgeon at our institution. Retrospective chart review was performed to gather preoperative and first postoperative (1PO) clinical presentation signs/symptoms and SF-36 scores as GQoL proxies. Prospective SF-36 scores will be collected to evaluate longitudinal GQoL outcomes. OQoL will be evaluated using the DC/TMD screening questionnaire.
Results: Preoperatively, compared to SBC, TS patients reported lower Physical functioning (∆= 27.3, p-value < 0.05), Social functioning (∆= 27.6, p-value < 0.05), Bodily Pain (∆= 32.6, p-value < 0.05) and General Health (∆=19.9, p-value < 0.05) SF-36 scores. In the first postoperative (1PO) SF-36, TS patients reported positive improvement in all domains, in particular demonstrating clinically significant improvement in Social Functioning. SBC patients reported only marginal improvement in the Mental Health domain. Clinical presentation for swallowing difficulties comparing Pre-op and 1PO revealed an absolute risk increase in SBC (15%, p< 0.05), whilst no TS patients reported swallowing complaints.
Conclusion : Although TS patients report lower SF-36 scores in all domains compared to SBCs, they report greater positive improvement following SPI surgery at 1PO. More recent SF-36 will be collected to provide longitudinal evaluation of GQoL. DC/TMD screening questionnaires will be collected to evaluate OQoL.
Methods: Between 2002 and 2022, 20 SBC patients and 14 TS patients were surgically managed by a single surgeon at our institution. Retrospective chart review was performed to gather preoperative and first postoperative (1PO) clinical presentation signs/symptoms and SF-36 scores as GQoL proxies. Prospective SF-36 scores will be collected to evaluate longitudinal GQoL outcomes. OQoL will be evaluated using the DC/TMD screening questionnaire.
Results: Preoperatively, compared to SBC, TS patients reported lower Physical functioning (∆= 27.3, p-value < 0.05), Social functioning (∆= 27.6, p-value < 0.05), Bodily Pain (∆= 32.6, p-value < 0.05) and General Health (∆=19.9, p-value < 0.05) SF-36 scores. In the first postoperative (1PO) SF-36, TS patients reported positive improvement in all domains, in particular demonstrating clinically significant improvement in Social Functioning. SBC patients reported only marginal improvement in the Mental Health domain. Clinical presentation for swallowing difficulties comparing Pre-op and 1PO revealed an absolute risk increase in SBC (15%, p< 0.05), whilst no TS patients reported swallowing complaints.
Conclusion : Although TS patients report lower SF-36 scores in all domains compared to SBCs, they report greater positive improvement following SPI surgery at 1PO. More recent SF-36 will be collected to provide longitudinal evaluation of GQoL. DC/TMD screening questionnaires will be collected to evaluate OQoL.
